Java vs JavaScript: Which One is Right for Your Next Project?

Introducing Java vs JavaScript: Object-oriented vs. non-object-oriented. There's been a steady debate brewing in developer circles in recent years about the best technology stack to use for building enterprise applications.
Do you go with the tried and true modern Java with its focus on enterprise business applications, or does JavaScript appeal to you – because of its ubiquity in web applications and UI interfaces?
Most companies already have strong preferences for a particular technology. But if they are kicking the tires and open to alternatives, there are undoubtedly many factors to consider. Most important are performance, integration, scalability, maintainability, and security.
For example, a financial services company might need to migrate its legacy mainframes to a microservices architecture and develop a mobile app for consumers. Or a fintech startup is pioneering in conversational banking and wants to know what language would be the best for building a voice-enabled app for consumers.
These are real problems and challenges for many companies today. In this article, we dig into the pros and cons of Java vs JavaScript (or, in our case, Node JS vs Java). This assessment is based on a scenario that arose a few years ago on a client project for a piece of middleware that applied data changes to the client's mobile application front-end. The client's architect team suggested we try NodeJS.
As a software development company specializing in full-stack .NET, Java, JavaScript, this started as a conversation about the pros and cons of each platform based on capabilities such as integration, performance, and maintainability.
We also discuss an integrated development environment and touch briefly on the debate over object-oriented vs. functional programming. This article is all the result of our ongoing conversation as a practice of continuous learning, friendly debate, and pride in each developer's "home language."
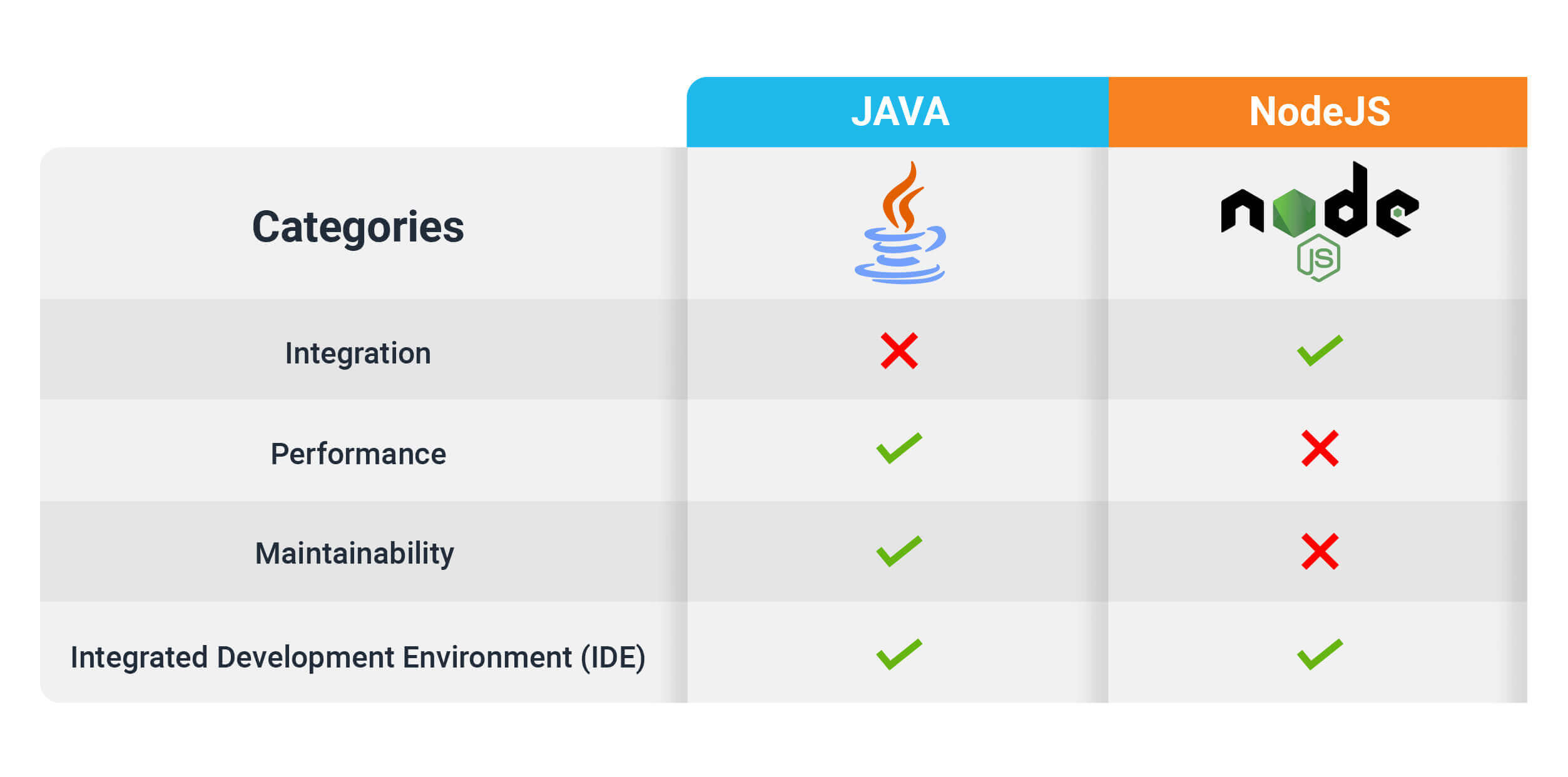
Java and JavaScript Integration: A Seamless Way to Build Powerful Web Applications
Software integration brings together discrete sub-systems to create a holistic, unified system. Integrated systems have better overperformance and are easier to manage.
 NodeJS
NodeJS
Pro:
- NodeJS is a good match for high-performance operations, including processing responses and systems requests.
- It works best without calculations, arithmetic equations, or CPU-intensive operations.
Con:
- Single-threaded event loops cannot compete with Java for handling multiple concurrent events, especially at high peak times like Black Friday.
Java
Pro:
- Provides better tools for manipulating workflow and integration layers.
- Stronger at complex workflows.
Con:
- Doesn’t match NodeJS for performance on matters of aggregation or integration layers.
WINNER
Choosing between Java or Javascript depends on the type of workflow complexity, though NodeJS edges out on overall integration capabilities.
JavaScript vs Java: A Performance Showdown
Performance is a metric that measures how fast a software operates, usually measured in terms of response time or throughput. Performance engineering has emerged in recent years within many organizations as a set of best practices to drive increased efficiencies in the SDLC process, especially for identifying bottlenecks earlier in development.
NodeJS
Pro:
- Better at managing synchronized operations for blocking requests.
- Java and other tools and frameworks would typically give good performance in this area but are too resource intensive.
Con:
- Sub-par performance for hashing algorithms, encryption, decryption, or CPU operations. Java, Python, and C# all have better tools for this.
- NodeJS can serve substantial user bases. However, in cases of high I/O or lengthy processes, it can experience delays and blocking requests in the background.
Java
Pro:
- Multi-threading feature enables simultaneous running of two or more parts of a program for maximum CPU utilization.
- Leads to better overall performance without heavy overhead or bottlenecks.
Con:
- To match Java’s efficiencies, NodeJS applied a clustering feature that enables users to create child processes that each run on their own single thread in order to handle high loads.
WINNER
Java*
 Node handles concurrent requests well since mega companies like Netflix and PayPal use NodeJS to build their server-side applications. However, there are a few points to consider:
Node handles concurrent requests well since mega companies like Netflix and PayPal use NodeJS to build their server-side applications. However, there are a few points to consider:
- NodeJS is not used on all their systems but only very specific components.
- Twitter underwent a major migration to Scala (Java).
- NodeJS is best served for I/O operations that are only a few microseconds. For instance, this applies in network applications where operation latency between request and response on the server side is as minimal as possible.
Java or JavaScript: Which Language is Easier to Maintain?
From a software development perspective, maintainability is defined as follows: "The ease with which a software system or component can be modified to correct faults, improve performance or other attributes, or adapt to a changed environment."
One approach to maintaining good code is to create clean code. To better understand the nature of maintainability, it's helpful to understand more about clean code.

A Java Recommendation System: Writing Clean Code
In software engineering, clean code refers to code that is easy to read and change. This seems simple enough, but there are a lot of complexities that arise when clean code is compared to both object-oriented and functional programming frameworks. Let’s break this down by pointing to how Java and JavaScript developers both approach clean code.
NodeJS
Pro:
- With increased adoption of NodeJS, more options and better tools are available for “clean code” best practices.
- JavaScript allows for more freedom to custom-build applications to your preferences.
Con:
- No strong clean code architecture references exist in JavaScript.
- There are a variety of JavaScript standards, but considerable differences exist for specific subtypes.
Java
Pro:
- Long-standing, large, open source community that is strong and stable.
- Stable enterprise software drive by Sun then Oracle and time-tested by many large companies over the years.
Con:
- Java perceived as stubborn and rigid regarding design principles, which can cause lots of boiler plate code to be added.

TypeScript (open source superset of JavaScript, which transcompiles to the language)
Pro:
- Enhances the readability of JavaScript code by ensuring modules and components are organized meaningfully.
- While TypeScript is not at the level of Java, it has enhanced JavaScript a lot and can become just as maintainable as Java.
Con:
- TypeScript can also be misused a lot, like Java or any object-oriented function.
WINNER
Java*
Even though Java can be a complex language, many developers are drawn to its maintainability. This means they will often challenge themselves by learning to separate the code to make it as future-proof, extendable, and maintainable as possible.
Exploring An Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
An IDE is a software application that provides computer programmers with a comprehensive framework for software development, often consisting of a source code editor, build automation tools and a debugger.
A favorite Integrated Development Environment used at Integrant is Visual Studio Code, a free source-code editor made by Microsoft for Windows, Linux, and macOS. It includes basic support for most programming languages.
We prefer VS Code over Jet Brains IDE as it easily enables users to view code quality, offers suggestions and alerts for common mistakes, and recommends splitting or dividing code functions.

Pro:
- Open source and free (don’t have to create a license).
- Small companies or people don’t have to pay, so they can dedicate more money to marketing and business development.
- Lightweight with many extensions.
Con:
- Does not come with smart suggestions for JavaScript
Modern Java Debate: Object-Oriented vs. Functional Programming?
A final point in this discussion concerns the object-oriented vs. functional programming debate. In various online tech forums, articles, and podcasts, this has become an ongoing point of discussion in recent years.
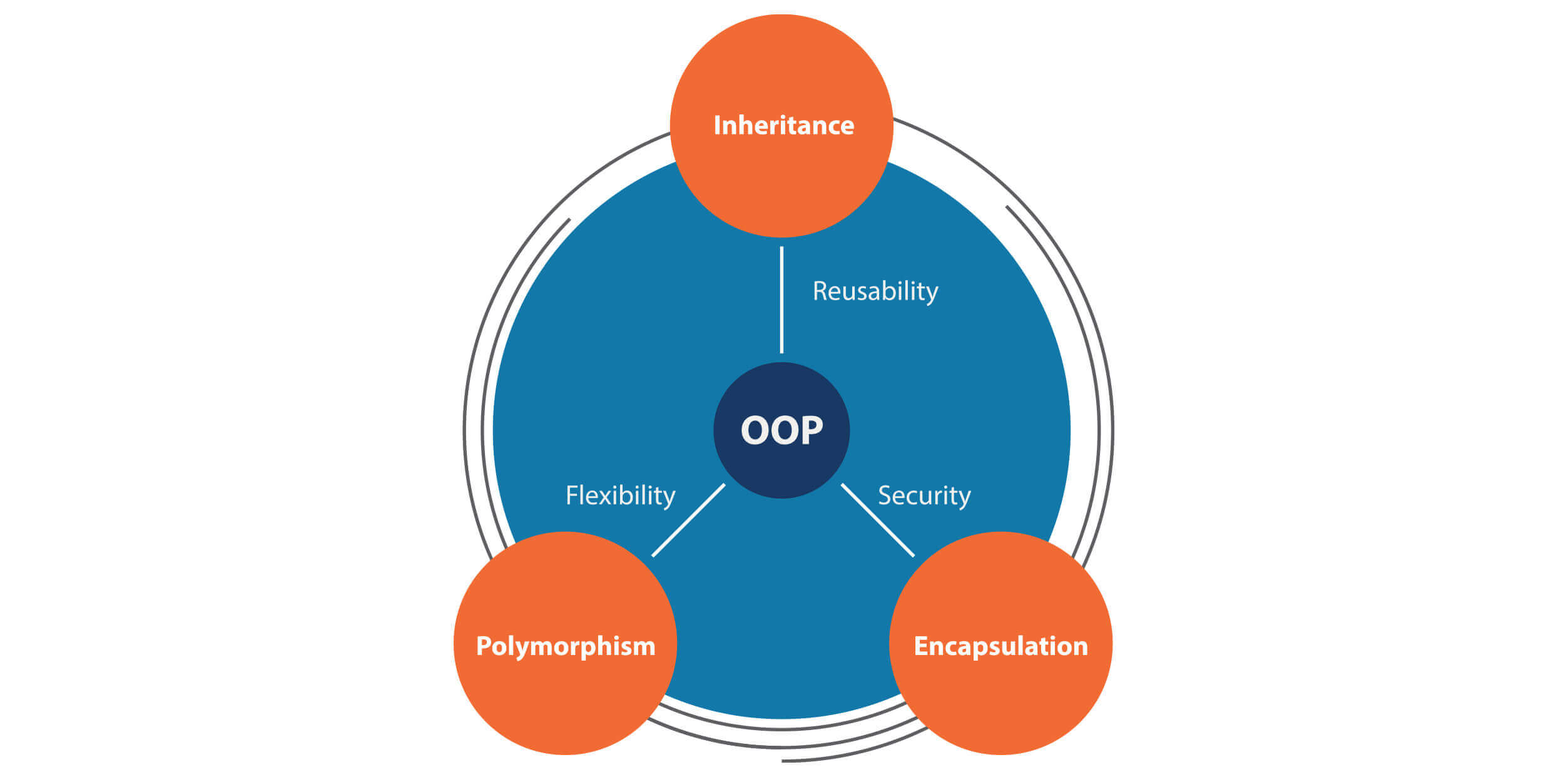
To object orient or not to object orient? Functional programming vs. object-oriented? Is one approach better than the other? As is often the case, the answer is – it depends! Here are the essential points to consider:
- Realize that your programming objectives can be achieved in several ways.
- Leverage the right team and skillsets to get the most out of your code.
- Functional programming inherits OOP concepts, creating a hybrid approach (new tipping point in the software industry).
- Background matters a lot when building a new application.
- NodeJS has a flat learning curve, but this still requires best practices for the language to ensure you’re building maintainable code.
- Java developers can easily pickup NodeJS – they already have the basics, including a solid predisposition for “clean code” best practices.
- NodeJS has a lot of frameworks for organically creating more clean code.
- We recommend List.js to help build clean, maintainable code in JavaScript.
Key Takeaways
Our engineers love a good debate. However, when it comes to software development and the question of Java vs JavaScript, we found that the answers aren’t so clear cut.
Following a client challenge a few years ago to explore JavaScript, we took the opportunity to dig in and explore NodeJS as a viable option for enterprise application development.

So what's the worst answer when it comes to debating Java vs JavaScript? It depends!
While Java was the winner for this particular project, when it comes to complex, multi-factored topics, the answer of which programming language is better will rely heavily on your business goals and desired solutions, along with any constraints, whether it's time, skillset, resources, and beyond. Check out our blog on Java and AI to learn more about Java's potential for your business.
JavaScript is perfect for modern network applications, while Java has traditionally focused on enterprise apps and core business logic. But the lines are blurring, and in the digital transformation era, each language is quickly being adopted to new use cases and contexts.
At Integrant, our mission is to help you achieve your business goals and become a digital-first company. Whether your preference is Java or JavaScript, we have the capabilities, skills, and expertise to help turn your vision into reality and build elegant and valuable solutions that please your customers. We would be more than happy to share a demo of our work!
Contact us today to learn how we can partner together on your next project.
